Gynecomastia (breast enlargement) in adolescents
During adolescence, a time when external looks start to really matter, there is often a development of gynecomastia, or feminine breast enlargement, in males.
The word gynecomastia originates from the Greek language and it means “feminine breasts”.
Despite this being a temporary condition that resolves spontaneously in most cases without any treatment, the condition can cause serious social embarrassment and may have a detrimental effect on the teenager’s self-imaging. It may even have psycho-social implications and can affect the adolescent’s social functioning.
The condition, investigations required and methods of management will be discussed below by Dr Asaf Olshinka, a pediatric plastic surgeon listed under my ‘recommended physicians’ and you can find more information about him here.
What is gynecomastia and why does it happen?
Gynecomastia is a condition where there is real breast tissue in male adolescents or in men, and it is usually caused by hormonal changes that occur during puberty. It is a very common condition and can occur in up to 50% of adolescents.
Why does it occur? During puberty, there is a secretion of male and female hormones (androgen and estrogen), both in boys and girls. Gynecomastia can occur due to a hormonal imbalance, in such a way that the effect of the female hormones becomes greater than that of the male hormones and triggers the breast to form extra tissue. If there is sufficient female hormone secretion, the breast tissue develops in a way that causes the breasts to look feminine.
This condition can be unilateral (one-sided), bilateral (both sides), symmetrical or asymmetrical.
Can there be any other causes to gynecomastia other than a temporary hormonal imbalance?
Although the common cause behind gynecomastia is a hormonal imbalance during adolescence, there can be other causes to the condition as well, such as certain diseases or medication side effects (for example, growth hormone which you can read more about here).
Additionally, it is important to distinguish between “real” gynecomastia and a condition that is referred to as “pseud-gynecomastia,” where the breast enlargement in males occurs as a result of weight gain, and not because of breast tissue enlargement (although the two conditions may look similar externally).
In the majority of cases, the reason behind feminine looking breasts is a combination of both enlarged tissue and being overweight.
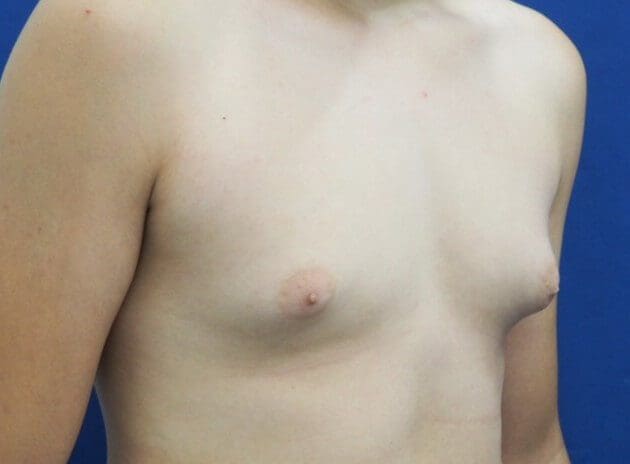
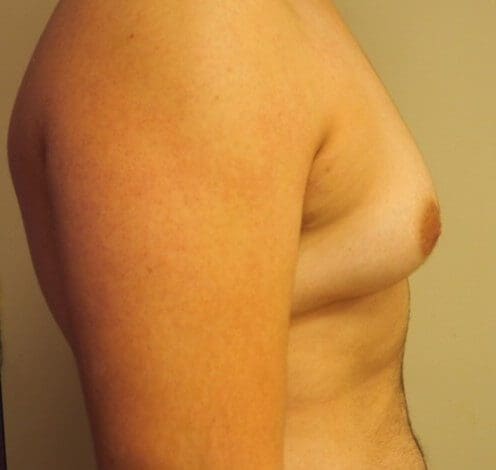
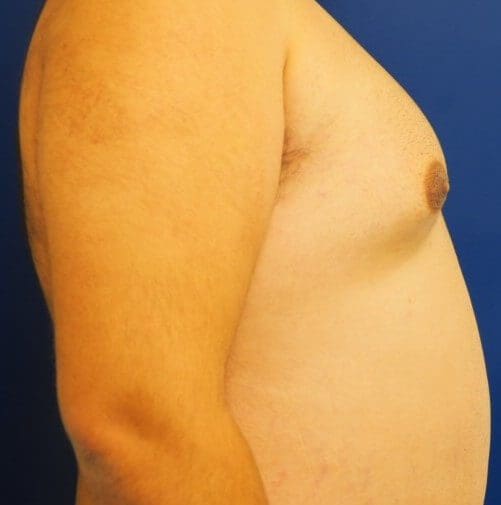
Take a look at the three images attached to this post. The first one shows a male with mild gynecomastia, with excess breast tissue visible below the nipple. In the second image we can see moderate gynecomastia with both excess breast tissue and excess fat tissue. The third image shows fatty gynecomastia – caused by obesity, read more here.
What are the investigations required for gynecomastia in adolescents?
Just like any other medical condition, this diagnosis requires a physician’s consult including a medical history and physical examination. In most cases, a primary care physician (either family physician or pediatrician) consult is sufficient. Certain scenarios require further investigations including blood tests for hormone levels and an endocrinologist consult. Another important medical tool that may be helpful is breast ultrasound.
What are the potential management options for gynecomastia in adolescents?
I’m going to cut to the chase. Although gynecomastia may be a very common condition in adolescents, in most (up to 75%) of the cases it improves on its own within 2 years. If it seems like one of the causes of the breast enlargement is patient obesity that has lead to pseudo-gynecomastia, then weight reduction through adequate diet and physical activity is the right way to go. Only if the gynecomastia remains even after the patient has reached their target body weight, treatment methods through surgical intervention may be considered (read more about this below).
Furthermore, there are certain cases that could benefit from pharmacological therapies that may help with the hormonal imbalance. However, it is important to note that pharmacological therapy is currently controversial as healthcare professionals have been unable to come to an agreement with regards to the adequate medications, recommended length of treatment and its efficacy.
Is there a surgical procedure for gynecomastia?
Surgery is the main method of treatment available for those cases that require intervention. The goal of surgery is to achieve breasts that are more ‘male’ looking, and at the same time, to leave minimal scarring. Plastic surgeries for gynecomastia are very effective. The procedure is offered to male patients whose breast shape has been consistent over the past year and who have undergone a full investigation that has yielded normal results.
What does the surgical procedure entail?
In mild conditions, where there is slightly excess fat tissue or breast tissue, it is possible to simply perform liposuction or breast tissue excision (usually, it is a combination of both), with the help of small incisions at the breast margins. If there is a significant excess of breast tissue and that is the main cause of the enlarged breasts, the excess breast tissue is resected in an open surgical procedure. The excision can either be isolated or may be performed together with liposuction. In an open surgical procedure, the incision is performed at a concealed site, either around the bottom margin of the breast or on the sides. The extra breast tissue and fat tissue are excised through this incision.
In certain severe cases excess skin is removed, as well, leaving longer scars on the surface of the breast.
Complications following surgery are rare but may include infection, bleeding, fluid retention, severe scar tissue, injury to the nipple and asymmetry of the two breasts. In addition, to reduce the swelling that occurs after the surgery, the patient must wear a compression vest for several weeks.
In summary, gynecomastia is a benign condition, characterized by enlarged breasts in a male due to overgrown breast tissue and/or fat tissue. Surgical treatment for breast reduction and excision of excess tissue may be available following a full medical workup. If you suspect you may be suffering from gynecomastia, and it is affecting your quality of life – seek medical attention for a professional consult!
For comments and questions, please register
