Teething in babies and children
What hasn’t been written about teething in babies? At what age? What is the correct order of teeth eruption? When to pay attention? When should you first go visit a dentist? And the most important thing – can a fever of 38.5 be attributed to teething?
In this post (written by the wonderful pediatric dentist – Prof. Esti Davidovich), you will find answers for all of these questions and more.
When to expect the first tooth?
You need to remember that a baby is born with a full set of primary teeth in his gums (“milk teeth”). Underneath are some of the permanent teeth. Teething of the first tooth begins around 6 months of age, but the time frame is very wide – from 3 months to a year.
Which tooth will erupt first? What is the correct order for the appearance of teeth?
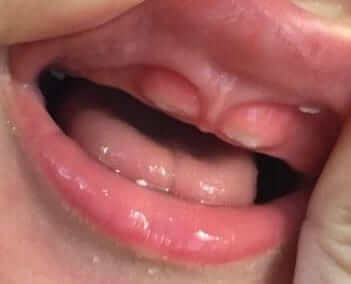
Usually the main incisors in the lower jaw (Mandible) will erupt first, and later on the upper incisors (see adjacent photo). The first molars will erupt around 1.5 years of age. Teeth will usually erupt in pairs, when the lower teeth will be first and the upper ones will follow.
The rate of eruption will differ from one baby to another, but the eruption of teeth will usually end until the baby is 2.5-3 years old. With the completion of the process there will be 20 primary teeth in his mouth.
Interesting fact – girls will start showing teeth eruption sooner than boys.
How (if even possible) can you identify tooth eruption in babies?
A few days before the eruption of the tooth you can see swelling in the gums and a white protuberance, which is in fact the tooth itself.
If there is a delay in teeth eruption – is there a problem?
Remember that teeth eruption occurs during a wide time frame, and in most cases early or late eruption does not suggest any medical problem. In most cases of late eruption, one of the parents will tell you he had the same problem as a baby.
Having said that – in cases of late teeth eruption you should go and get evaluated by your pediatrician / pediatric dentist. What will he or she look for? Mainly nutritional deficiency or hypothyroidism. Remember that most of the time there will not be a hidden disease. You will just have to be a bit patience.
What symptoms are related to teething and what are not?
Many different symptoms and illnesses are attributed to teething. It could be because the age when babies are beginning teething is also the age when they start to contract many viral infections. It may be a bit disappointing, but good quality scientific studies have shown that teething (especially incisors), can cause a mild elevation of fever in babies, but not above 38.0. Also, there is no correlation between teething and many systemic symptoms such as diarrhea, runny nose or cough.
But, if a mother swears that every time before another tooth erupts there is a certain medical phenomena that she recognizes as related to teeth eruption, than I will accept her opinion. Not everything is written in the text books.
What symptoms are known to be related to teeth eruption? Restlessness, salivating and sensitivity in the gums.
What treatment can be given to relief pain or restlessness from teeth eruption?
Since teeth eruption can cause pain and discomfort, you can give the baby paracetamol or ibuprofen. In terms of local treatment, teethers or local ointments for relief can be considered.
Teethers – the cold surface of the teether causes vasoconstriction of the blood vessels in the gums, which reliefs’ pain. In addition, the biting action itself causes local pressure that sooths the pain.
Local ointments – products that are designated for local use to relief pain and irritation from teeth eruption. These products are in gel form, and are divided into two main groups:
Products that are based on natural active ingredients such as: hyaluronic acid, calendula oil, saffron, fennel, aloe vera, olive oil, ginger and chamomile. Some believe these products are giving mild relief, but I’m still part of the old school physicians that claims that the effectiveness of these products are extremely limited and are mostly an unnecessary expense.
Products that contain anesthetic (Benzocaine) – products like this, that were intended for preventing pain while teething are banned for use today, especially for children under 2 years. Usage may cause methemoglobinemia – a condition when the ability of the hemoglobin to carry oxygen in the blood is compromised.
At what age permanent teething begins and at what age it ends?
It being on average around 6 years, and it ends around 13 years. In permanent teeth, the first ones to erupt are also the lower incisors.
At what age should a child be evaluated by a pediatric dentist?
Most of the international societies of dentistry for children recommends a first visit at the pediatric dentist within 6 months after the eruption of the first tooth or at the age of one.
The goal is not to treat the teeth, but to give recommendations that can help prevent dental diseases in the future. If you want to read more on how to maintain oral hygiene in children, just click here.
For comments and questions, please register
